XCP Server Protocol
XCP Overview
XCP (Universal Measurement and Calibration Protocol) is a communication protocol standardized by ASAM (Association for Standardization of Automation and Measuring Systems). It enables external tools to interface with ECUs for the purposes of measurement and calibration. XCP is transport-independent, making it adaptable across various communication interfaces such as CAN, Ethernet, FlexRay, LIN, and SxL (SPI and SCI).
The protocol is widely adopted in the automotive and embedded industries due to its flexibility, standardization, and cross-platform compatibility. XCP enables engineers to access internal ECU parameters, observe real-time behavior and tune calibration parameters without recompilation.
Transport Layer Abstraction
XCP operates independently of the physical layer by defining a standardized command set and memory access protocol. Its abstraction model separates the protocol logic from the transport medium, allowing developers to switch between different interfaces (e.g., from CAN to Ethernet) with minimal changes to the upper layers.
Key Capabilities
Measurement: Read internal signals, variables, and memory locations in real time without halting ECU execution.
Calibration: Modify parameters during runtime for optimization and validation, including tuning of control logic.
Memory Access: Perform safe memory read/write operations for debugging, development.
Event and DAQ-Based Acquisition: Enables scheduled or triggered data acquisition for time-synchronized logging.
RAPIDSEA XCP Stack
Embien offers XCP Stack for server configurations. Our implementation supports the standard commands defined by the protocol over the Ethernet transport layer.
Some of the salient features of RAPIDSEA XCP protocol stack are :
Supports standard XCP commands for calibration, measurement, and memory access.
Implements polling-based data acquisition using standard
SHORT_UPLOADandDOWNLOADcommands.Lightweight, embeddable design suited for real-time environments and compatible with linux.
The implementation can be configured in server mode and is completely flexible.
XCP Server
RAPIDSEA implements an XCP slave that allows a client tool to connect and communicate with it to perform calibration, measurement, and memory access operations
Supported Functionalities
Following commands are supported in the XCP Stack
Command Code |
Command Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
0xFF |
CONNECT |
Initializes a session with the XCP client and establish a connection. |
0xFE |
DISCONNECT |
Terminates the current session with the XCP client |
0xFD |
GET_STATUS |
Returns the current state of the server, including session and resource status. |
0xFC |
SYNCH |
Used to maintain synchronization between client and server. |
0xFB |
GET_COMM_MODE_INFO |
Provides communication configuration details and optional features. |
0xF6 |
SET_MTA |
Sets the Memory Address (MTA), which points to the memory address used by upload/download operations. |
0xF4 |
SHORT_UPLOAD |
Reads a small block of memory directly from the server using the previously set MTA (Memory Transfer Address). |
0xF0 |
DOWNLOAD |
Writes a block of data from the client to server’s memory at the current MTA(Memory Transfer Address) location. |
0xDD |
START_STOP_SYNC |
Starts or stops server-side DAQ (Data Acquisition) processes in synchronous (polling) mode. |
Application Interface
While the RAPIDSEA XCP server stack can handle most of the functionality such as client request validation, if it has error request, proper intimation to the client. The RAPIDSEA XCP server clearly defines API and callback functions that are essential for the user to use/implement.
The below table captures the primary function that are to be called from the application logic.
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
rs_xcp_server_open |
To Initialize the serial/socket configuration. |
rs_xcp_server_run |
To set the state to be open |
rs_xcp_server_process |
To be called periodically to prepare the client response. |
The below table contains rcb calls to perform the server stack.
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
rcb_xcp_server_connect |
Called when a CONNECT command is received from the client. Initializes session, displays connected mode and sets default parameters |
rcb_xcp_server_disconnect |
Called when a DISCONNECT command is received. Used to terminate the active session |
rcb_xcp_server_get_status |
Called to report current status of the XCP session, including session flags and event states |
rcb_xcp_server_sync |
Called when a SYNC command is received. Used to synchronize polling-based data acquisition |
rcb_xcp_server_get_comm_mode_info |
Called to return communication mode capabilities and configuration supported by the server |
rcb_xcp_server_set_mta |
Called to set the Memory Transfer Address (MTA) pointer for subsequent upload or download operations |
rcb_xcp_server_short_upload |
Called to write a short block of data into the memory address specified by the MTA |
rcb_xcp_server_download |
Called to read data from the memory address set via MTA. |
rcb_xcp_server_start_stop_synch |
Called to start or stop polling-based data acquisition as requested by the client |
rcb_xcp_server_unknown_command |
Called when an unsupported or unknown command is received. Used for error handling |
Implementation Guide
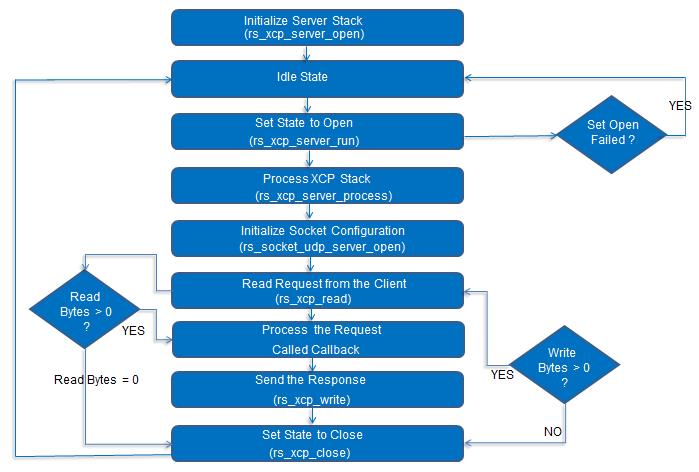
This section explains how to implement the XCP server stack using the RAPIDSEA stack, the steps to be followed are
Initially start the XCP server task from the application layer.
Then the server task state is in idle condition, until the XCP server starts.
XCP server starts change the state from the idle to state open.
In XCP server process, process the client requested command, process it and prepare the response for the client.
In case of a requesting failing or invalid command, error code will be sent from the server as response.
The below diagram captures the high level sequence of operations associated with the XCP server.
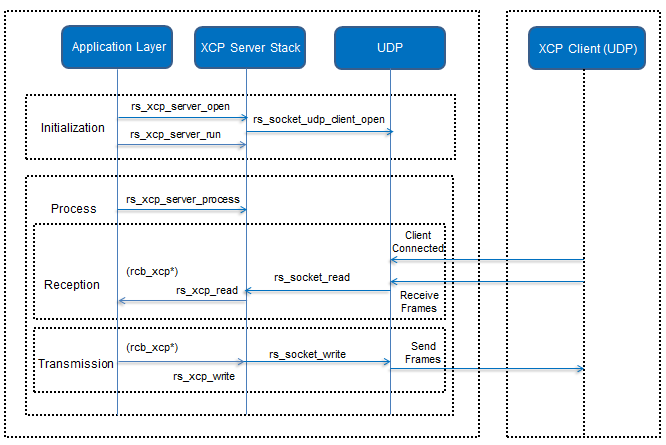
High level flow chart is depicted below for XCP server:
XCP Supported Modes
XCP UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
This version of the XCP protocol is implemented for communication over UDP/IP networks linking over port 5555. XCP over UDP allows faster and connectionless data exchange. No additional checksum is implemented at the protocol level. XCP messages are encapsulated directly within UDP datagrams for efficient real-time access to ECU memory for measurement and calibration.
Socket communication header details refer to the socket interface page for more details Socket Interface
XCP Server Stack Memory Usage
The XCP server stack has the size of bytes
XCP server stack RAM consumption
The RAM consumption is different for the each of the interfaces.
Interface |
Size |
|---|---|
UDP |
bytes |
XCP Server header Details
Documentation from the relevant server header as follows :
Warning
doxygenfile: Cannot find file “rs_xcp_server.h