SOME/IP Server Stack
Overview
RAPIDSEA supports SOME/IP protocol as explained in the SOME/IP Protocol page. This page explains the server architecture and details how the user should interface the stack with their custom logic and realize the ECU implementation quickly. It also provides guidelines on adopting the stack for different systems.
The below diagram captures the block level diagram of the SOME/IP server and how it interfaces with other modules.
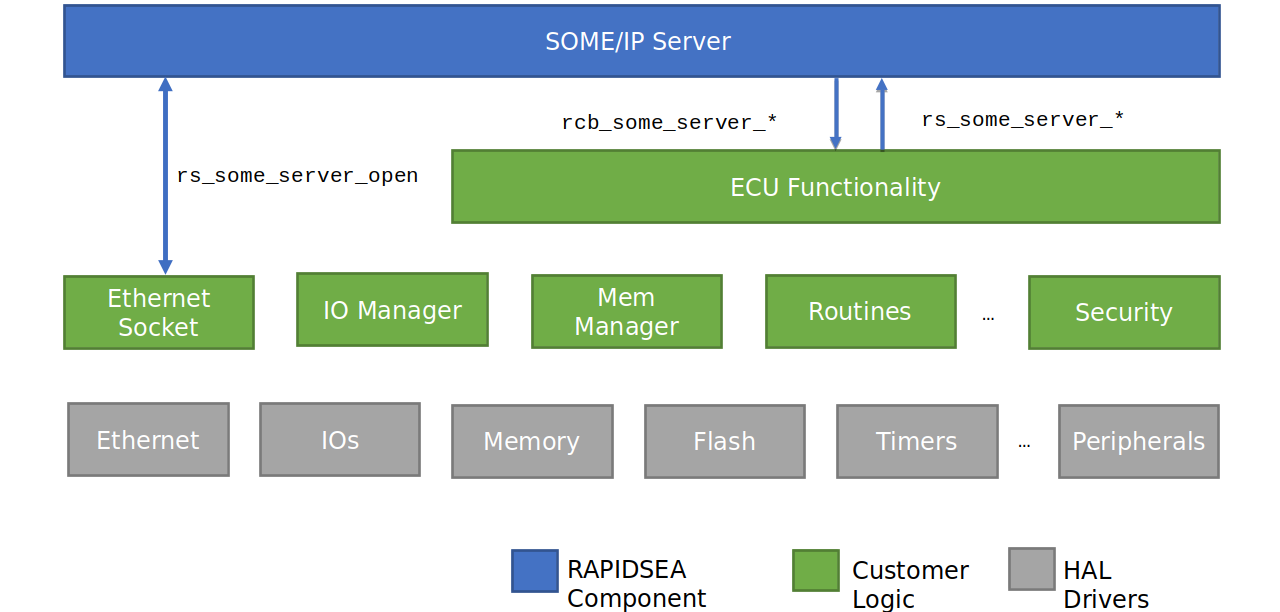
Application Interface
While the RAPIDSEA SOME/IP server stack can handle most of the functionality such as message validation, service discovery management, subscription handling, Notification process etc, the business logic has to implement the application functionality. the RAPIDSEA SOME/IP server clearly defines API and callback functions that are essential for the user to use/implement.
The below table captures the function that are to be called from the application logic.
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
rs_some_server_open |
To initialize the SOME/IP server instance structure for both discovery and notification process. |
rs_some_server_run |
To be called to set the run state for state machine for both discovery and notification process. |
rs_some_server_set_tx_msg_buf |
To set up the transmit buffers to be used for the SOME/IP server communication. |
rs_some_server_set_rx_msg_buf |
To set up the receive buffers to be used for the SOME/IP server communication. |
rs_some_server_req_stop_offer_service |
To frame and sent the stop offer service from server |
rs_some_server_process |
To be called to call the discovery and notification’s state machine and process respectively and notification event send function. |
rs_some_server_subscribe_init |
To initialize the SOME/IP subscription details structure associated with the server |
rs_some_server_set_reboot_flag |
To be called to set the reboot flag in SOME/IP server instance. |
rs_some_server_send_notify_event |
To be called to send notification events from server |
rs_some_server_close |
To freed the SOME/IP server handle |
There are many functions through which the SOME/IP server stack retrieves information from the application logic or indicate actions to be performed. These functions are captured in the below table.
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
rcb_some_server_rx_req_handler |
called to handle the request received from client and prepare the response |
rcb_some_server_update_response_status_info |
Called to send the update value as notification message to client. |
rcb_some_server_get_serialized_config_option |
called to check service available or not and registered if available. |
rcb_some_server_get_load_balancing_option_info |
Called to get the data of load balancing option |
rcb_some_server_set_deserialize_config_option |
Called to set the deserialized data of configuration option |
rcb_some_server_get_mem |
Called to get memory |
SOME/IP Server Configuration Parameter:
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
server_addr |
SOME/IP Server IP address |
sd_multicast_addr |
SOME/IP SD Multicast IP address |
sd_port |
SOME/IP SD Port number |
protocol_ver |
SOME/IP protocol version |
interface_ver |
SOME/IP interface version |
initial_delay |
SOME/IP SD initial wait time |
repetitions_base_delay |
SOME/IP SD repetition base delay |
repetitions_max |
SOME/IP SD repetition max |
sd_ip_version |
SOME/IP SD IP Version (IPv4/IPv6) |
log_level |
SOME/IP Client log level |
These functions are documented in detail in the below sections. It is important for the server to implement these functions correct for proper operation of the system.
Implementation Guide
This section explains how the SOME/IP server can be implemented using the RAPIDSEA stack. The stack is available in source form, the steps to be followed are
Initialize the server configuration.
Implement the Callback functions mentioned above
Initialize the buffers necessary for the operation
Initialize the SOME/IP stack function.
Periodically call the rs_some_server_process functions so that internal timeouts are handled.
High level flow chart is depicted below:
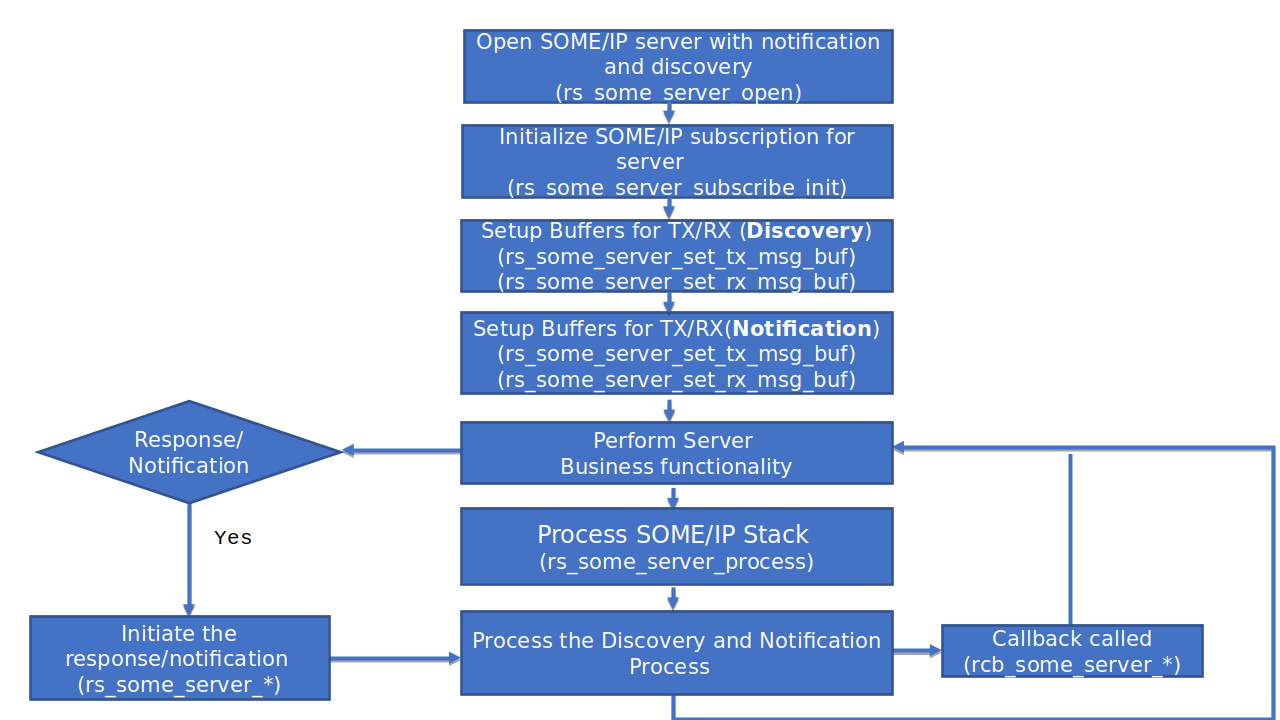
The below diagram captures the high level sequence of operations associated with the SOME/IP stack.

This can be implemented in a bare-metal system or over RTOS or over full fledged OS such as Linux etc.
SOME/IP Server Stack Memory Usage
Platform |
Memory |
Size |
|---|---|---|
Linux |
ROM |
105KB |
Linux |
RAM |
40KB |
Micro controller (iMXRT) |
ROM |
110KB |
Micro controller (iMXRT) |
RAM |
160KB |
Platform |
Memory |
Size |
|---|---|---|
Linux |
ROM |
118KB |
Linux |
RAM |
230KB |
Micro controller (iMXRT) |
ROM |
280KB |
Micro controller (iMXRT) |
RAM |
255KB |
Note:
The above table captures the memory usage for five services. Each service has two or one event groups, and across these eventgroups, a total of ten events are mapped. If you add or remove services, the memory usage will increase or decrease accordingly.
Dependency
This stack depends on the below RAPIDSEA interfaces that can be obtained or custom implemented.
Example demo
An example implementation is available along with the release and is described in SOME/IP Server Demo.
SOME/IP Server Header Details
Documentation from the relevant header as follows:
Warning
doxygenfile: Cannot find file “rs_someip_server.h