ISO15765 - DoCAN Protocol
DoCAN Overview
ISO 15765 (ISO-TP or DoCAN) is an international standard for sending data packets over a CAN-Bus that exceed the eight byte maximum payload of CAN frames. ISO-TP segments longer messages into multiple frames, adding metadata that allows the interpretation of individual frames and reassembly into a complete message packet by the recipient allowing up to 4GB of transfers.
Embien offers its implementation of the protocol via the RAPIDSEA DoCAN stack. Some of the major features of the stack are
Support for both SF, FF, CF and FC
Support for various timing configuration
Multi-message filtering
Up to 4095 bytes transfer support
MISRA-C compliant ANSI C source code
Can be used with or without RTOS
Can support 8, 16, 32, 64-bit CPUs
As captured in the below diagram, the DoCAN stack is typically accessed by the higher level application stack like UDS and this in-turn calls the lower level CAN HAL.
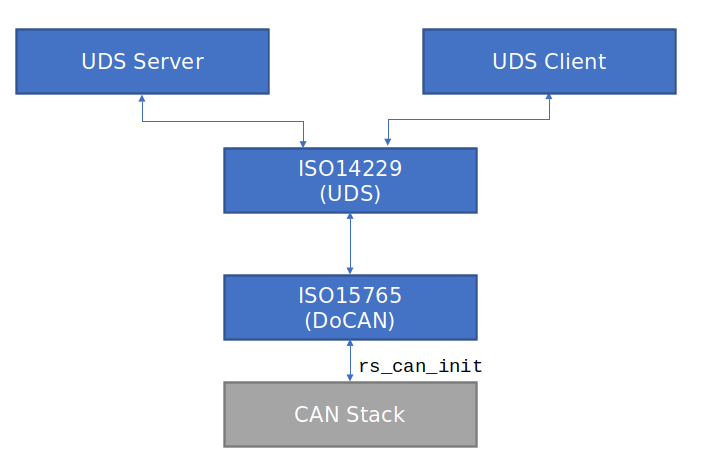
Using DoCAN
This section covers the details of how to use the DoCAN stack. Essentially the DoCAN is responsible for framing of packets and de-framing of packets of large messages over smaller CAN frames. It employs frames such as SingleFrame (SF), FirstFrame(FF), ConsecutiveFrame(CF) and FlowControl(FC) packets to manage the message flow.
As it is message oriented, the RAPIDSEA DoCAN stack has to be provided with the buffers during initialization. The size of the buffers can be determined by the user based on their application requirement. For example, if 4096 message size has to be supported, each of the buffer must be of at least this size plus a few more.
When the higher level application layer wants to transfer a message, it should first request one from the DoCAN layer, fill it with data and queue it for transmission. Then the DoCAN stack sends the message over one or more frames and informs the caller of the status of the transfer. Similarly when an incoming message is received, DoCAN consolidates it over multiple frames in a single message and provides it to the application layer as a single message.
The below table captures the function that are to be called from the application logic.
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
rs_iso15765_open |
To initialize the ISO15765 DoCAN stack |
rs_iso15765_set_tx_msg_buf |
To assign buffers for transmission |
rs_iso15765_set_rx_msg_buf |
To assign buffers for reception |
rs_iso15765_release_transmit_msg |
To release the transmit buffer of DoCAN message |
rs_iso15765_rx_buffer_handled |
To indicate successful processing of received message |
rs_iso15765_register_callback |
Registers callback function to be called on events |
rs_iso15765_process |
To be periodically called for internal processing |
rs_iso15765_close |
To free the DoCAN handle |
The details of these functions are covered in the below sections.
The application logic should call the rs_can_init function and use the returned handle when initializing the DoCAN stack.
The below table captures the function that are called from the DoCAN Stack.
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
rs_can_register_callback |
Registers the ISO15765 DoCAN stack call back with the CAN layer |
rs_can_get_transmit_buf |
To get CAN buffers for transmission |
rs_can_transmit |
To transmit CAN buffers |
More details of these CAN related functions are available in the CAN Interface page.
The below diagram captures the high level sequence of operations associated with the DoCAN stack.
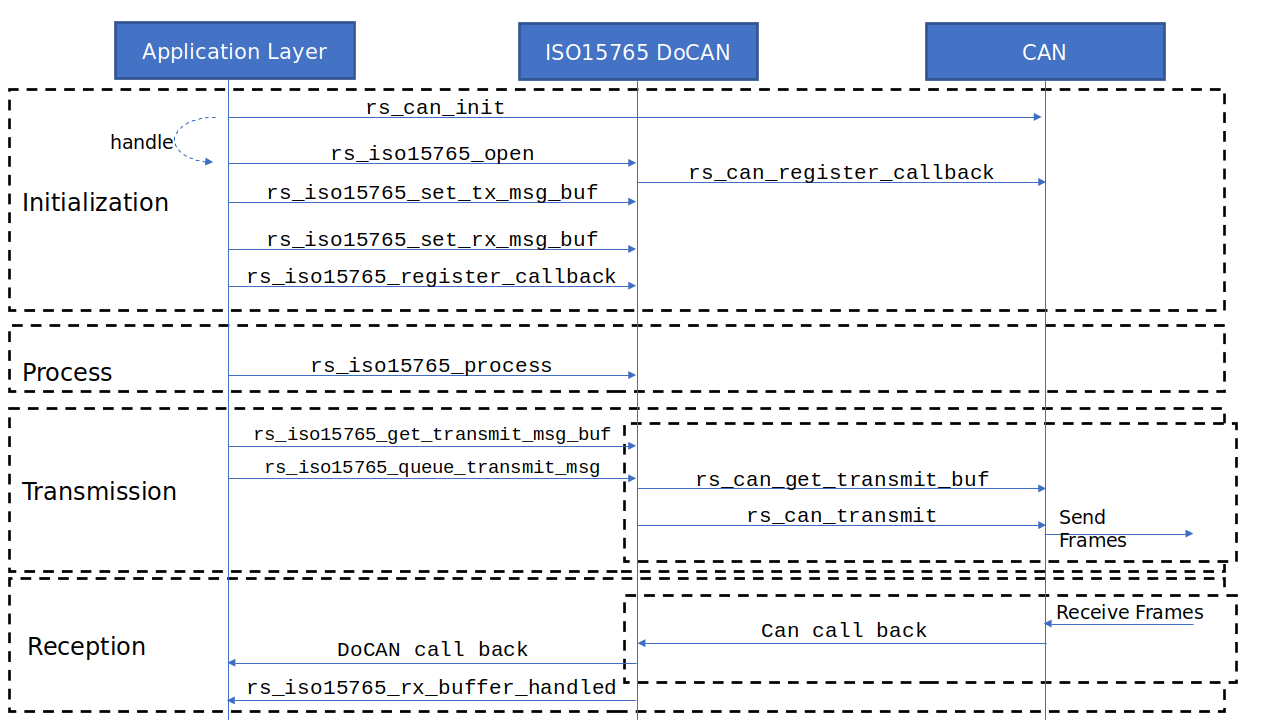
Refer to the ISO14229 - UDS Protocol page for an example about how the RAPIDSEA UDS stack uses the DoCAN.
Dependency
This stack depends on the below RAPIDSEA interfaces that can be obtained or custom implemented.
DoCAN Header Details
Documentation from the relevant header as follows:
Warning
doxygenfile: Cannot find file “rs_iso15765.h