Auto Modules Introduction
The RAPIDSEA Automotive Modules provide a comprehensive suite of features for managing automotive data such as speedometer, tachometer, odometer, tripmeter, fuel gauge, and temperature readings. These modules use an efficient moving average filter for processing the data.
The following modules are supported in RAPIDSEA:
Overview
The Automotive application primarily involves:
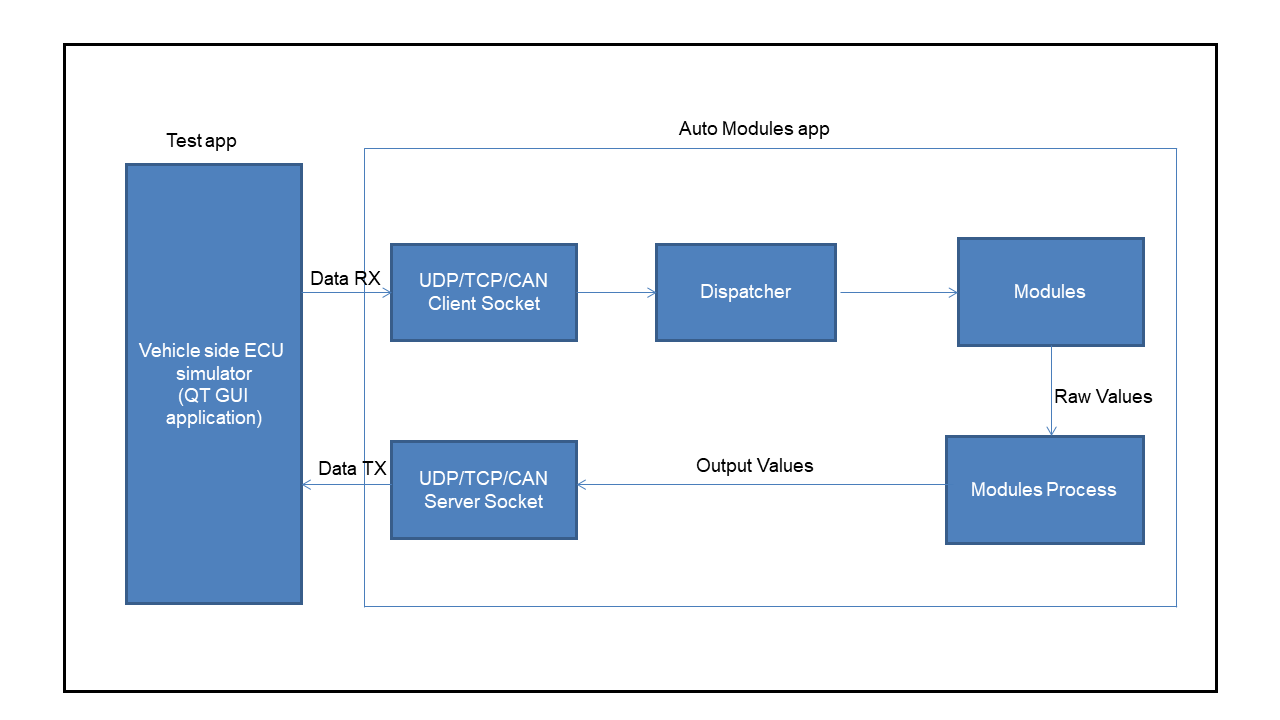
Configuring modules such as the speedometer, trip meter, tachometer, odometer, and others with scaling factors, thresholds, and other parameters.
Receiving and processing from UDP/TCP/CAN data for automotive modules.
Displaying processed data to the user interface through registered callbacks.
Auto Modules Data Structures
The RAPIDSEA Automotive Modules provide a robust and flexible solution for managing and monitoring automotive data. By using a set of well-defined configuration, runtime, and output structures, these modules enable seamless integration into the vehicle’s ECU. Whether you are tracking speed, temperature, fuel, or other vital vehicle parameters, RAPIDSEA’s modules offer efficient processing, real-time data monitoring, and diagnostic capabilities to ensure vehicle performance and safety.
Structure |
Description |
|---|---|
am_config_t |
Each module has a configuration structure that stores the setup and initialization parameters. This includes module enable or disable, the module’s CAN ID for communication, settings for signal types (analog/digital), and any other configuration parameters that are essential for the module’s operation. |
am_runtime_t |
The runtime structure stores dynamic and real-time data that changes during the vehicle’s operation. It holds values received from sensors, processed values, and the current state of the system. |
am_output_t |
The output structure contains the final values that represent the module’s status. This may include output data for indicators or signals that the module controls or monitors. |
rs_am_t |
Finally, each module is encapsulated in a global structure, which integrates the configuration, runtime, and output structures. This structure allows for easy access to all of the data related to the module and provides a central point for management. |
Auto Modules Working Processes
The Auto Modules in RAPIDSEA follow a structured process to efficiently manage and monitor vehicle data. Here’s a simple overview of how the modules work:
Configuration Phase - Each module is configured using the am_config_t structure.
Data Collection - The module collects real-time data from ECU (e.g., speed, temperature, fuel level). This data is stored in the am_runtime_t structure for processing.
Data Processing - The collected data is processed using algorithms like the moving average filter to smooth out any fluctuations. The processed data is then stored in the same runtime structure.
Output Generation - After processing, the module generates output values (e.g., current speed, fuel level) stored in the am_output_t structure.
Communication - The final processed output is sent back to the Vehicle ECU Simulator via a UDP socket. This allows the vehicle dashboard or simulator to display the data in real-time
Error Codes
Each API for the filter moving average module returns success or failure codes. For detailed information on the error codes, please refer to the following section:
See also
Conclusion
The RAPIDSEA Automotive Modules provide a comprehensive and flexible solution for real-time data monitoring, diagnostics, and performance tracking in modern vehicles. By leveraging robust data structures and efficient processing algorithms (such as the moving average filter), RAPIDSEA enables seamless integration with a vehicle’s ECU. These modules empower automotive manufacturers with the tools needed for effective data management, system diagnostics, and user interface control.
Auto Module Header Details
The header file for the Auto module, rs_am.h, defines the overall Auto modules required structures and APIs for initialization and processing.
Warning
doxygenfile: Cannot find file “rs_am.h