OBD-II Client Stack
OBD-II Client Overview
RAPIDSEA supports ISO15031 protocol as explained in the ISO15031 - OBD Protocol page. This page explains the client architecture and details how the user should interface the stack with their custom logic and realize the Tester implementation quickly. It also provides guidelines on adopting the stack for different systems.
The below diagram captures the block level diagram of the DoCAN OBD-II client and how it interfaces with other modules.
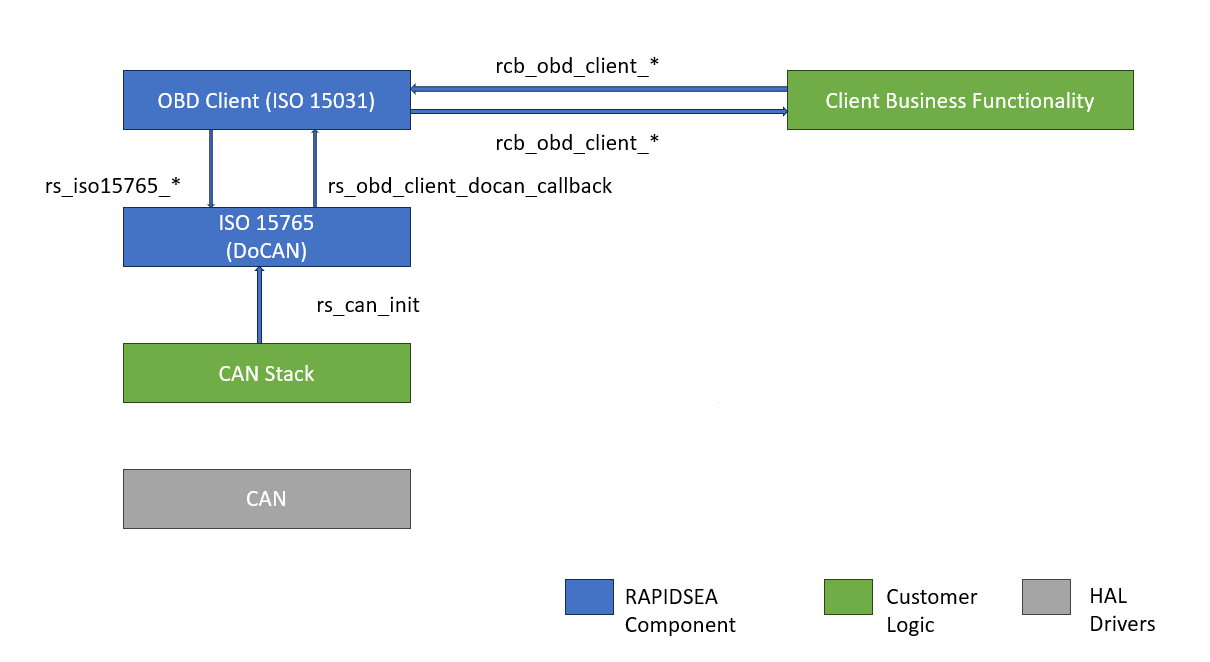
DoCAN Interface
The OBD-II client communicates over the CAN network through the underlying DoCAN stack (ISO15765). This DoCAN stack is also available as part of the RAPIDSEA components. All the functions that are needed are available as part of the DoCAN stack and has to be compiled together.
Mode |
Description |
|---|---|
rs_iso15765_* |
Set of functions called by OBD-II client to perform operation such as initialize, transmit messages etc |
rs_obd_client_docan_callback |
Callback function called by the DoCAN layer to inform of Data Indication, error etc |
These details with respect to the DoCAN interface are covered in detail in the ISO15765 - DoCAN Protocol page.
Application Interface
While the RAPIDSEA OBD-II client stack can handle most of the functionality such as message validation, session management, timing control etc, the business logic has to implement the application functionality. The RAPIDSEA OBD-II client clearly defines API and callback functions that are essential for the user to use/implement.
The below table captures the function that are to be called from the application logic.
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
rs_obd_client_open |
To initialize the OBD-II client stack |
rs_obd_client_process |
To be called periodically to process the incoming/outgoing messages |
rs_obd_client_enable_pos_resp_suppression |
To enable/disable positive response suppression |
There are many functions through which the OBD-II client stack retrieves information from the application logic or indicate actions to be performed. These functions are captured in the below table.
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
rcb_obd_client_01h_current_diagnostic_data_resp |
Called when response for a default session setup request is received |
rcb_obd_client_02h_freeze_frame_data_resp |
Called when response for a freeze frame data request is received |
rcb_obd_client_03h_diag_trouble_code_resp |
Called to read DTC information by various report types |
rcb_obd_client_04h_clear_reset_dtc_resp |
Called when response for clear DTC request is received |
rcb_obd_client_05h_oxygen_sensor_test_results_resp |
Called when response for oxygen sensor test request is received |
rcb_obd_client_06h_on_board_monitoring_results_resp |
Called when response for on board monitoring results request is received |
rcb_obd_client_07h_emission_dtc_current_cycle_resp |
Called when response for emission DTC current cycle request is received |
rcb_obd_client_08h_on_board_system_resp |
Called when response for on board system request is received |
rcb_obd_client_09h_vehicle_information_resp |
Called when vehicle information request is received |
These functions are documented in detail in the below sections. It is important for the client to implement these functions correct for proper operation of the system.
Implementation Guide
This section explains how the OBD-II server can be implemented using the RAPIDSEA stack. Whether the stack is available in source form or in binary form, the steps to be followed are
Implement the Callback functions mentioned above
Implement the underlying rs_can_* functions for DoCAN as per the underlying hardware design as described in the CAN Interface page.
Initialize the buffers necessary for the operation
Initialize the CAN, ISO15765 and SAE ISO15031 stack function for DoCAN and OBD-II.
Periodically call the process functions so that internal timeouts are handled.
If there is a need to send a request to ECU/server, send via rs_obd_client_req_* calls such as rcb_obd_client_04h_clear_reset_dtc_resp etc.
On reception of negative response from server, rcb_obd_client_error_resp function is called.
Up on successful completion of transmission of request or failure to do so, rcb_obd_client_transmit_confirm is called with relevant reason code.
High level flow chart is depicted below for DoCAN:
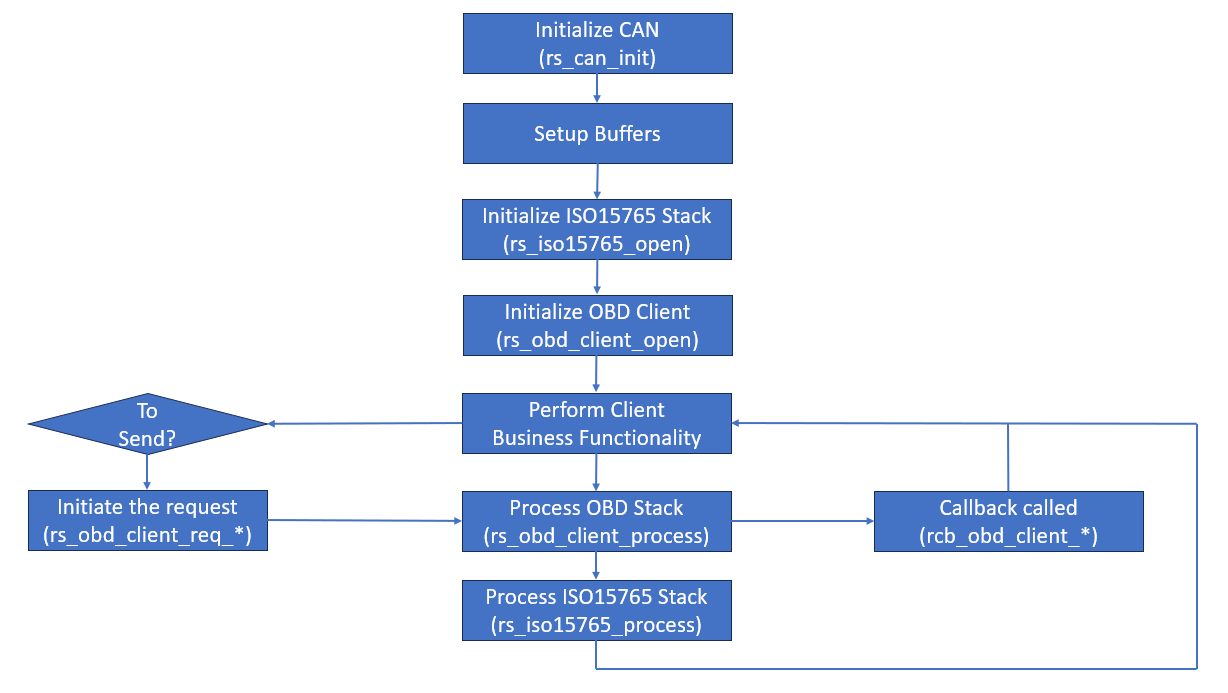
This can be implemented in a bare-metal system or over RTOS or over full fledged OS such as Linux etc.
Dependency
This stack depends on the below RAPIDSEA interfaces that can be obtained or custom implemented.
Example demo
An example implementation is available along with the release and is described in DoCAN OBD-II Client Demo.
OBD-II Client Header
Documentation from the relevant header as follows:
ISO15031 OBD Client Module.
This file contains the APIs for using ISO15031 defined OBD server module
- Author
Embien RAPIDSEA Team
- Copyright
Embien Technologies India Pvt. Ltd.
Defines
-
RS_OBD_CLIENT_MAX_NUM_RX_MSGS
Number of receive messages that can be buffered during reception.
Typedefs
-
typedef struct tag_rs_obd_client_config rs_obd_client_config_t
Contains information about client configuration.
-
typedef struct tag_rs_obd_client_instance rs_obd_client_instance_t
Contains information about client.
Functions
-
rs_handle_t rs_obd_client_open(rs_obd_client_instance_t *ptr_instance, rs_obd_client_config_t *ptr_config)
Initializes the OBD client stack.
This function initializes the OBD stack for client operation
- Parameters:
ptr_instance – [in] - Pointer to the OBD client instance
ptr_config – [in] - Pointer to the OBD client configuration
- Returns:
Handle of the OBD client instance information which include configuration information also
-
rs_ret_val_t rs_obd_client_process(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle)
Function to be called periodically to process underlying OBD client state machines.
This function is to be called at not more than 5 ms interval
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
- Returns:
Zero on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rcb_obd_client_transmit_confirm(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, rs_ret_val_t reason)
Called when there is an update on the last transmit request.
This function is called when the server updates the successful delivery of last request or failure to do so
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client
reason – [in] - Update reason such as RS_ISO15765_SERVICE_COMM_DATA_CONFIRM, RS_ISO15765_SERVICE_COMM_N_TIMEOUT_A etc
- Returns:
Zero on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rcb_obd_client_error_resp(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_service, uint8_t u8_error_code)
Called when the server responds with error for a request.
This function is called when the server returns error for a request
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client
u8_service – [in] -Service code that failed such as RS_ISO15031_SI_ECU_RESET
u8_error_code – [in] - Error code such as RS_ISO15031_NRC_CONDITIONS_NOT_CORRECT, RS_ISO15031_NRC_GENERAL_PROGRAMMING_FAILURE etc
- Returns:
Zero on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rs_obd_client_req_current_diag_data(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_pid_number)
Request Current Diagnostic Data.
This function Request the Current Diagnostic Data
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
ptr_instance – [in] - Pointer to the UDS client instance
u8_pid_number – [in] - Requested PID number
- Returns:
Return 0 on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rs_obd_client_request_freeze_frame_data(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_pid_number)
Request freeze frame data.
This function Request freeze frame data
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
ptr_instance – [in] - Pointer to the UDS client instance
u8_pid_number – [in] - Requested PID number
- Returns:
Return 0 on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rs_obd_client_req_diag_trouble_code(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_pid_number)
Request diagnostic trouble code.
This function Request the diagnostic trouble code
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
ptr_instance – [in] - Pointer to the UDS client instance
u8_pid_number – [in] - Requested PID number
- Returns:
Return 0 on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rs_obd_client_req_clear_reset_dtc(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_pid_number)
Requests Clear DTC for the server.
This function initiates clear DTC request for the given type
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
ptr_instance – [in] - Pointer to the UDS client instance
u8_pid_number – [in] - Requested PID number
- Returns:
Return 0 on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rs_obd_client_req_oxygen_sensor_test_results(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_pid_number)
Request the oxygen sensor test results.
This function Request the oxygen sensor test results
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
ptr_instance – [in] - Pointer to the UDS client instance
u8_pid_number – [in] - Requested PID number
- Returns:
Return 0 on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rs_obd_client_req_on_board_monitoring_results(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_pid_number)
Request on board monitoring test results.
This function request and retrieve test results from an onboard monitoring system, ensuring that relevant data is collected for analysis, diagnostics, or reporting
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
ptr_instance – [in] - Pointer to the UDS client instance
u8_pid_number – [in] - Requested PID number
- Returns:
Return 0 on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rs_obd_client_req_emission_dtc_current_cycle(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_pid_number)
Request emission DTC for the current cycle.
This function requests the emission diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) for the current cycle from the OBD system.
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
u8_pid_number – [in] - Requested PID number
- Returns:
Return 0 on success or an error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rs_obd_client_req_control_on_board_system(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_pid_number)
Request control for on board system.
This function request and execute control commands or adjustments for an onboard system, allowing remote or automated management of the systems operations.
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
ptr_instance – [in] - Pointer to the UDS client instance
u8_pid_number – [in] - Requested PID number
- Returns:
Return 0 on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rs_obd_client_req_vehicle_information(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_pid_number)
Request vehicle information.
This function request and retrieve vehicle information using OBD-II Service ID 9. This service is used to obtain detailed vehicle data, which can include VIN, calibration information, and other identifiers.
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
ptr_instance – [in] - Pointer to the UDS client instance
u8_pid_number – [in] - Requested PID number
- Returns:
Return 0 on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rcb_obd_client_01h_current_diagnostic_data_resp(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_err_code, uint8_t *ptr_data_record, uint32_t u32_data_len)
Requests the current diagnostic data.
This function sends a current diagnostic data request (0x01) to read the current diagnostic data from the OBD system.
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
u8_err_code – [in] - Error code received, if any
ptr_data_record – [in] - Pointer to the memory with list of data ID and value returned
u16_resp_len – [in] - Number of bytes of data read
- Returns:
Zero on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rcb_obd_client_02h_freeze_frame_data_resp(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_err_code, uint8_t *ptr_data_record, uint32_t u32_data_len)
Requests freeze frame data.
This function sends a request (0x02) to retrieve freeze frame data from the OBD system, which captures vehicle parameters at the time a diagnostic trouble code was stored.
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
u8_err_code – [in] - Error code received, if any
ptr_data_record – [in] - Pointer to the memory with list of data ID and value returned
u16_resp_len – [in] - Number of bytes of data read
- Returns:
Zero on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rcb_obd_client_03h_diag_trouble_code_resp(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_err_code, uint8_t *ptr_data_record, uint32_t u32_data_len)
Requests diagnostic trouble codes.
This function sends a request (0x03) to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes from the OBD system, which indicates any issues detected.
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
u8_err_code – [in] - Error code received, if any
ptr_data_record – [in] - Pointer to the memory with list of data ID and value returned
u16_resp_len – [in] - Number of bytes of data read
- Returns:
Zero on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rcb_obd_client_04h_clear_reset_dtc_resp(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_err_code, uint8_t *ptr_data_record, uint32_t u32_data_len)
Requests to clear or reset diagnostic trouble codes.
This function sends a request (0x04) to clear or reset any stored diagnostic trouble codes in the OBD system.
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
u8_err_code – [in] - Error code received, if any
ptr_data_record – [in] - Pointer to the memory with list of data ID and value returned
u16_resp_len – [in] - Number of bytes of data read
- Returns:
Zero on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rcb_obd_client_05h_oxygen_sensor_test_results_resp(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_err_code, uint8_t *ptr_data_record, uint32_t u32_data_len)
Requests oxygen sensor test results.
This function sends a request (0x05) to retrieve the results of oxygen sensor tests from the OBD system, which helps in monitoring the performance of the oxygen sensors.
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
u8_err_code – [in] - Error code received, if any
ptr_data_record – [in] - Pointer to the memory with list of data ID and value returned
u16_resp_len – [in] - Number of bytes of data read
- Returns:
Zero on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rcb_obd_client_06h_on_board_monitoring_results_resp(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_err_code, uint8_t *ptr_data_record, uint32_t u32_data_len)
Requests on-board monitoring results.
This function sends a request (0x06) to retrieve results of on-board monitoring tests from the OBD system, which assess the performance of various vehicle systems.
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
u8_err_code – [in] - Error code received, if any
ptr_data_record – [in] - Pointer to the memory with list of data ID and value returned
u16_resp_len – [in] - Number of bytes of data read
- Returns:
Zero on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rcb_obd_client_07h_emission_dtc_current_cycle_resp(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_err_code, uint8_t *ptr_data_record, uint32_t u32_data_len)
Requests emission-related DTCs for the current cycle.
This function sends a request (0x07) to retrieve emission-related diagnostic trouble codes for the current cycle from the OBD system.
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
u8_err_code – [in] - Error code received, if any
ptr_data_record – [in] - Pointer to the memory with list of data ID and value returned
u16_resp_len – [in] - Number of bytes of data read
- Returns:
Zero on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rcb_obd_client_08h_on_board_system_resp(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_err_code, uint8_t *ptr_data_record, uint32_t u32_data_len)
Requests on-board system information.
This function sends a request (0x08) to retrieve information about on-board systems from the OBD system.
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
u8_err_code – [in] - Error code received, if any
ptr_data_record – [in] - Pointer to the memory with list of data ID and value returned
u16_resp_len – [in] - Number of bytes of data read
- Returns:
Zero on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rcb_obd_client_09h_vehicle_information_resp(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_err_code, uint8_t *ptr_data_record, uint32_t u32_data_len)
Requests vehicle information.
This function sends a request (0x09) to retrieve vehicle-specific information such as VIN or calibration data from the OBD system.
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
u8_err_code – [in] - Error code received, if any
ptr_data_record – [in] - Pointer to the memory with list of data ID and value returned
u16_resp_len – [in] - Number of bytes of data read
- Returns:
Zero on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rs_obd_client_enable_pos_resp_suppression(rs_handle_t obd_client_handle, uint8_t u8_do_suppress)
Enables suppression of positive response from server.
This function can be used to disable/enable suppression of positive response messages from server
- Parameters:
obd_client_handle – [in] - Handle to the OBD client instance
u8_do_suppress – [in] - Non-zero value to suppress and zero not to suppress
- Returns:
Zero on success or error code on failure
-
rs_ret_val_t rs_obd_client_close(rs_handle_t obd_handle)
Function to free the OBD handle.
This function used to free the OBD handle
- Parameters:
obd_handle – [in] - Handle of the client instance information
- Returns:
Return 0 on success or error code on failure
-
struct tag_rs_obd_client_config
- #include <rs_obd_client.h>
Contains information about client configuration.
Public Members
-
uint8_t state
-
uint8_t state
-
struct tag_rs_obd_client_instance
- #include <rs_obd_client.h>
Contains information about client.
Public Members
-
rs_handle_t tp_handle
Transport Handle with corresponding type (DoIP/ DoCAN).
-
rs_obd_client_config_t *ptr_obd_client_config
Pointer to the OBD client configuration.
-
rs_buffer_mgr_t rx_msg_mgr
RX message FIFO.
-
void *arr_rx_msgs[RS_OBD_CLIENT_MAX_NUM_RX_MSGS]
Pointer array to hold incoming messages.
-
void *ptr_handlers
List of Client service handlers.
-
uint8_t pos_resp_suppress
Enable/disable positive response suppression.
-
uint8_t num_handlers
Number of Client service handlers.
-
rs_search_mgr_t si_search_mgr
Search manager for service handlers.
-
rs_handle_t obd_handle
Transport Handle to the OBD client instance.
-
rs_handle_t tp_handle