Modbus Client Protocol
MODBUS Overview
Modbus is a communication protocol used to transmit data across serial lines between various electronic devices. The protocol is open-source and can be used for major in industrial applications such as PLCs, variable speed drives, HMIs, Data acquisition systems etc. This is probably utilized for the connection of a system controlling using an RTU in SCADA in the power domain.
Embien offers Modbus Stack for both use in server and client configurations. Our implementation supports all the function codes defined by the protocol and supports extension via APIs too. Physical layers supported include RTU, ASCII and TCP/IP.
- Some of the salient features of RAPIDSEA Modbus protocol stack are
Single/Multiple Read/Write functionalities.
Coils/Holding Registers and Input Registers.
Supports major baud rates from 9600 to 115200 bauds and beyond
RTU/ASCII modes can be operated with and without parity and configurable Stop bits.
Server and Client Mode of operation.
Royalty Free Licensing Model.
Highly Optimized for MCU’s.
Uses less amount of RAM and ROM.
Runs on Linux, Windows and with/without RTOS.
The implementation is fully configurable and is offered for both server and client mode of operation.
Modbus Client
RAPIDSEA implements Modbus client where different types of requests such as READ_HOLDING, WRITE_INPUT etc can be orginated to the server address configured.
Supported Functionalities
Following services are supported in the Modbus Stack
Function Code |
Register Type |
Value Type |
Access Type |
|---|---|---|---|
01 (0x01) |
Read Coil Status |
Discrete |
Read |
02 (0x02) |
Read Input Status |
Discrete |
Read |
03 (0x03) |
Read Holding Registers |
16 Bit |
Read |
04 (0x04) |
Read Input Registers |
16 Bit |
Read |
05 (0x05) |
Write Single Coil |
16 Bit |
Read |
06 (0x06) |
Write Single Holding Register |
16 Bit |
Write |
15 (0x0F) |
Write Multiple Coils |
Discrete |
Write |
16 (0x10) |
Write Multiple Holding Registers |
16 Bit |
Write |
Application Interface
While the RAPIDSEA Modbus client stack can handle most of the functionality such as server response validation, validate client request formation, once submit the request, properly release the given request,etc. The RAPIDSEA Modbus client clearly defines API and callback functions that are essential for the user to use/implement. The below table captures the function that are to be called from the application logic.
The below table contains API calls to perform the client stack.
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
rs_modbus_client_open |
To Initialize the serial/socket configuration. |
rs_modbus_client_run |
To set the state to be open |
rs_modbus_client_process |
To be called periodically to process the request. |
rs_modbus_client_get_free_req |
To get a free available request from Modbus channel. |
rs_modbus_client_submit_req |
To submit the given request for the given channel. |
rs_modbus_client_is_req_done |
To return the current status of the given request. |
rs_modbus_client_put_req |
To release the given request for further use. |
rs_modbus_client_reconfig |
To restart the client application by reconfiguring modbus client. |
rs_modbus_client_close |
To close the Modbus client. |
rcb_modbus_serial |
Called to handle serial timeouts |
Only a millisecond timer is sufficient for the stack to run.
Implementation Guide
This section explains how to implement the Modbus client stack using the RAPIDSEA stack, the steps to be followed are
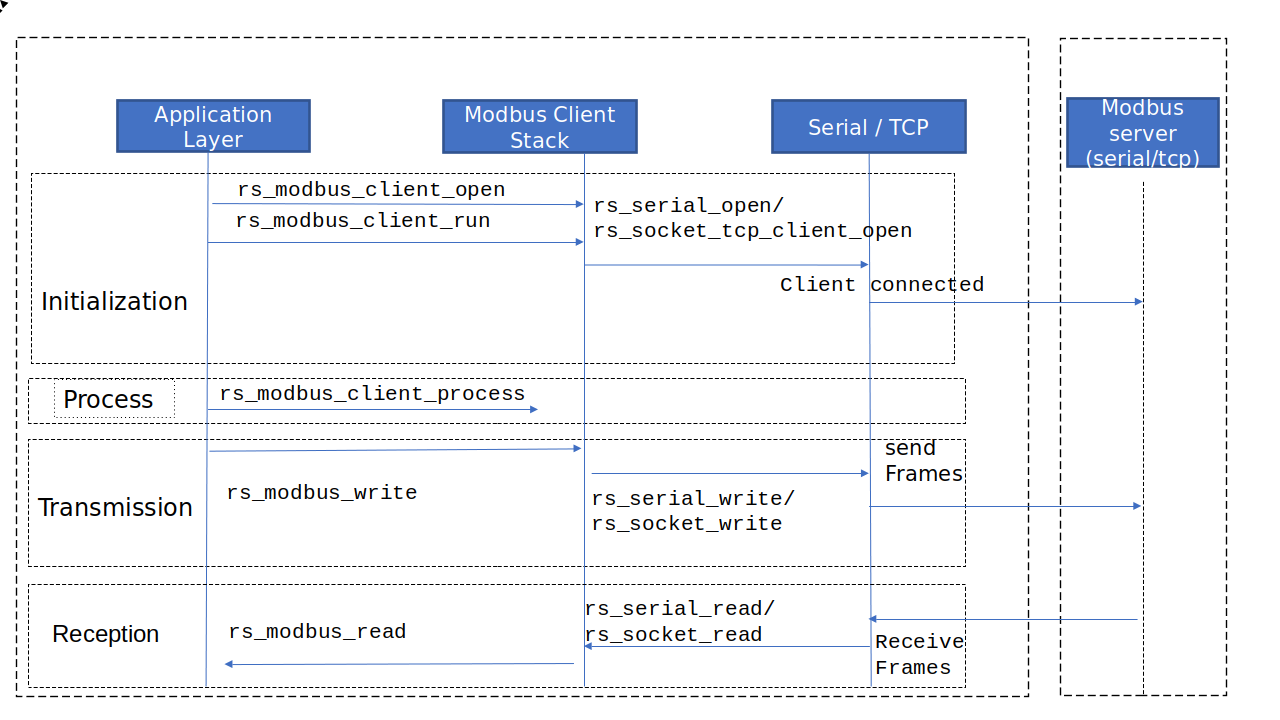
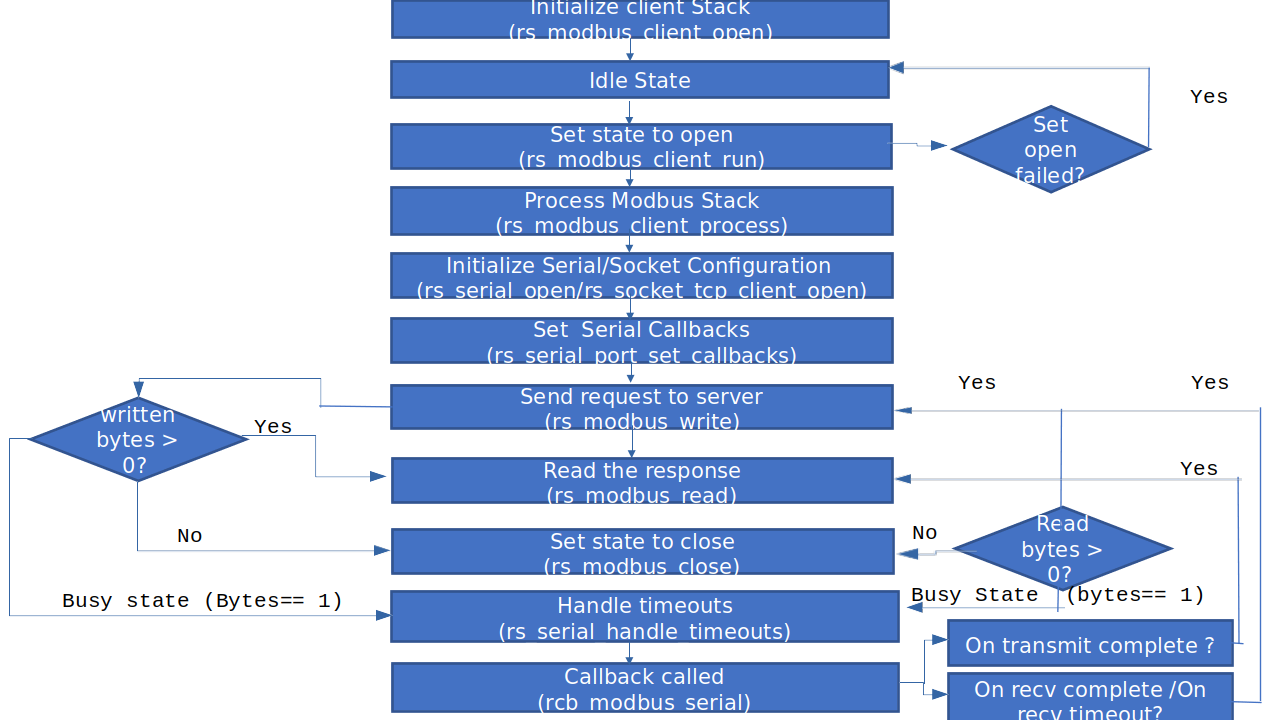
Initially start the client init to start the Modbus stack.
Then client task state is in idle condition, until Modbus client start.
Modbus client start change the state from idle to state open.
In Modbus client process, initially get the free available request from the Modbus channel by giving the Modbus handle.
Modbus client process called periodically to form the client request.
Once form the request, Submit the given request to the given channel.
Properly release the given request for further use.
The below diagram captures the high level sequence of operations associated with the Modbus client RTU
High level state machine of modbus client is depicted below
Modbus Supported Modes
Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit)
To establish protocol communication, this represents data in a binary format and is mostly utilized in serial communication. The messages in this version are divided by idle periods. The format that is followed in the RTU version is a cyclic redundancy check to verify mechanism and this makes sure of data reliability.
Serial communication header details refer to the serial interface page for more details Serial Interface
Modbus TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol)
To establish protocol communication, this represents data in a binary format and is mostly utilized in internet communication. The messages in this version are divided by idle periods. The format that is followed in the TCP version is a longitudinal redundancy check to verify mechanism and this makes sure of data reliability.
Socket communication header details refer to the socket interface page for more details Socket Interface
Modbus Client Stack Memory Usage
Modbus Client stack has the size of 28780 bytes.
Modbus Client Stack RAM Consumption
The RAM consumption is different for each of the interfaces.
Interface |
Size |
|---|---|
RTU |
964 bytes |
ASCII |
1736 bytes |
TCP |
372 bytes |
RTU Interface
- The memory (944 bytes) needed can be separated as follows:
256 bytes - buffer space for RX/TX in Modbus
256 bytes - buffer space for handling the RX FIFO buffer by the interface layer
256 bytes - buffer space for handling the TX FIFO buffer by the interface layer
196 bytes - other configuration related memory
ASCII Interface
- The memory (1736 bytes) needed can be separated as follows:
513 bytes - buffer space for RX/TX in Modbus
513 bytes - buffer space for handling the RX FIFO buffer by the interface layer
513 bytes - buffer space for handling the TX FIFO buffer by the interface layer
197 bytes - other configuration related memory
TCP Interface
- The memory (372 bytes) needed can be separated as following:
260 bytes - buffer space for RX/TX in Modbus
112 bytes - other configuration related memory
Modbus Client Header Details
Documentation from the relevant client header as follows:
Warning
doxygenfile: Cannot find file “rs_modbus_client.h