Automotive Navigation Stack
Overview
Modern clusters provide a rich set of features giving vehicle and environment information to the driver in an easy to consume way. One such feature that is desired for a two-wheeler/four-wheeler cluster is the connectivity to mobile App by which it enables viewing incoming call information, accepting/rejecting calls etc. Another desired feature is the navigation support, by which the user can feed in the destination and the route information is shown in the cluster as Turn-By-Turn (TBT) or map.
RAPIDSEA Automotive Navigation and Connectivity (ANC) Stack enables OEMs/Tier-1s to integrate these functionalities readily.
Supported features
RAPIDSEA ANC Stack supports the following features
Call Notifications
Message Notifications
Other Application Notifications
Call responses (accept/reject)
Music Control
Contact Details and Call logs
Turn by Turn
Map Mirroring
Weather indications
Update Cluster settings
Update Communication module WIFI and BLE name
It supports integration with both Android and iOS Apps.
Architecture
To lower the cost of the cluster processing engine, RAPIDSEA ANC enables connectivity with mobile App using a dedicated WiFi/BLE communication module. The below diagram depicts the stack with its underlying physical connection along with higher level modules.
The below diagram captures the high level block diagram of the RAPIDSEA ANC components and how it interfaces with other modules.
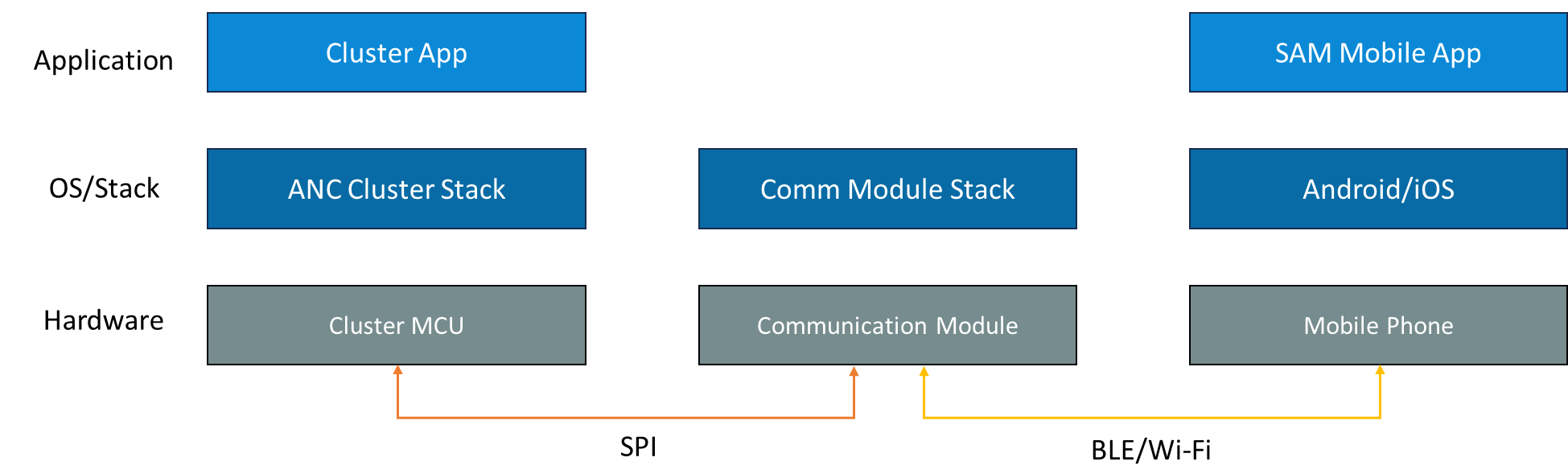
As it can be seen, the Cluster MCU and the Communication module is interfaced over SPI where the module communicates with the mobile phone over BLE or Wi-Fi. At the higher level the Cluster application integrates the Cluster ANC stack which abstracts the communication all the way down to the Smart Automotive Manager (SAM) mobile application.
RAPIDSEA ANC stacks components seamlessly takes care of the communication and allows developers to concentrate only on consuming the relevant data.
Hardware Interface
Data transmission between the cluster and communication module takes place over SPI with the cluster acting as SPI master. Apart from the CS, CLK, MISO and MOSI pins for SPI communication, two more pins are used for handshake purposes. The ClusterDataReady is an output from the cluster that indicates the master is ready with some data that needs to be transmitted to the communication module. The CommModuleReceiveReady is an input to the cluster to indicate the communication module is ready to send/receive data from the cluster.
The below diagram captures the hardware connectivity diagram of the components.
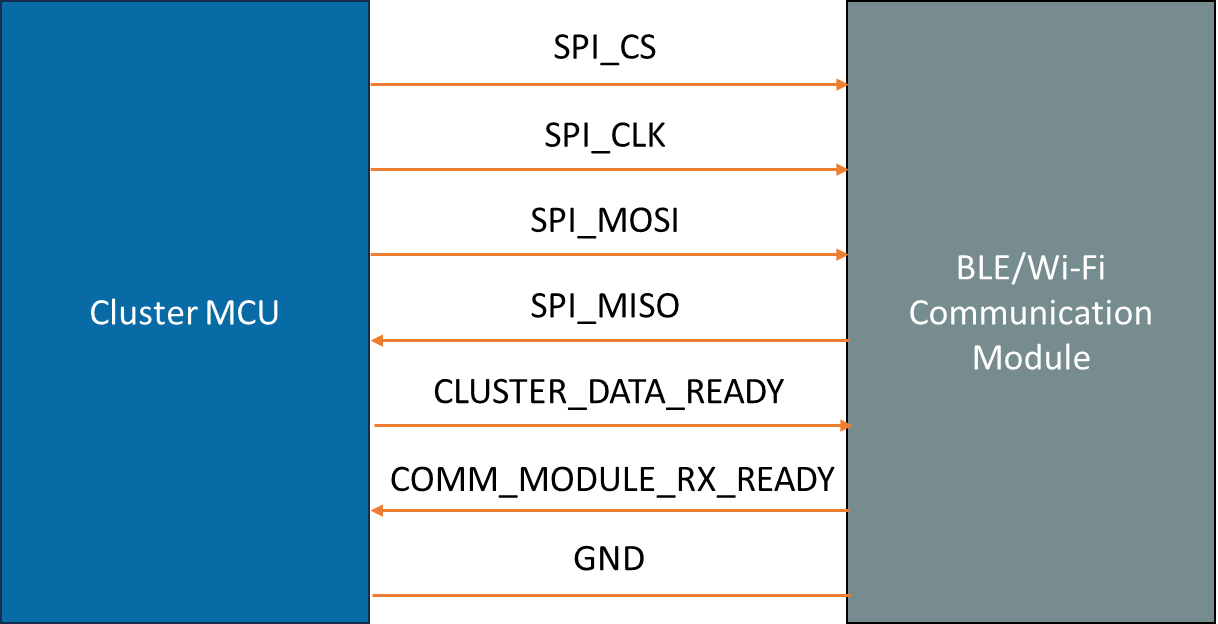
So, when the cluster is ready to send data, it sets the ClusterDataReady high and wait for the CommModuleReceiveReady to be asserted by the module. Only after it is high, the SPI transactions are initiated.
Similarly, when the communication module wishes to send data to the cluster, it sets CommModuleReceiveReady high. The cluster upon finding this high, sets the ClusterDataReady and initiated a transfer with an idle frame to the module simultaneously receiving the data from it.
After successful data transaction, both the handshake pins are set to low.
Application Interface
The RAPIDSEA ANC stack completely abstract the underlying communication with the communication module and the mobile app by providing a set of API functions and callbacks.
The below table captures the function that are to be called from the application logic.
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
rs_anc_open |
To initialize the ANC stack |
rs_anc_process |
To handle the ANC stack operation |
rs_anc_c2m_handle_call |
To handle the call notification |
rs_anc_c2m_contact_set_filter |
Assign the contact filter for further fetch request |
rs_anc_c2m_contact_get_by_index |
Request contacts by index |
rs_anc_c2m_contact_get_count |
To fetch contact count |
rs_anc_c2m_dial_by_index |
Dial the selected contact |
rs_anc_c2m_dial_call_log |
To dial the selected contact from the call log |
rs_anc_c2m_handle_other_call |
Handle the non-phone calls |
rs_anc_c2m_music_ctrl |
To send the music player control events |
rs_anc_c2m_music_volume_ctrl |
To send the music player volume control |
rs_anc_c2m_call_redial |
Redial recent call |
rs_anc_c2m_send_vehicle_data |
To update the vehicle data in the mobile |
rs_anc_c2m_fetch_call_log |
To fetch the call log |
rs_anc_c2m_dial_by_number |
To dial the given number |
rs_anc_c2m_change_ble_name |
To update the BLE publish name |
rs_anc_c2m_change_wifi_name |
To update the WiFi publish name |
There are many functions through which the ANC stack indicate actions to be performed. These functions are captured in the below table.
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
rcb_anc_c2m_req_failed |
Called to indicate failed requests |
rcb_anc_m2c_call_notification |
Called to indicate incoming call notification |
rcb_anc_m2c_wifi_map_data |
Called to indicate that a map data is received |
rcb_anc_m2c_other_call_handled |
Called to indicate incoming non-phone calls |
rcb_anc_m2c_calender_event |
Called to indicate calendar events |
rcb_anc_m2c_weather_info |
Called to indicate weather information update |
rcb_anc_m2c_date_time |
Called for time and date update |
rcb_anc_m2c_brightness |
Called for brightness update |
rcb_anc_m2c_find_vehicle |
Called for finding vehicle |
rcb_anc_m2c_vehicle_unlock |
Called to unlock vehicle |
rcb_anc_m2c_tbt_info |
Called to indicate for TBT information update |
rcb_anc_m2c_doc_download |
Called to indicate response for contact list requests |
rcb_anc_m2c_ble_status |
Called to update BLE status |
rcb_anc_m2c_wifi_status |
Called to update Wi-Fi status |
rcb_anc_m2c_msg |
Called to indicate message notification |
rcb_anc_m2c_music_status |
Called to update music player status |
rcb_anc_m2c_contact_count |
Called to report total contact count |
rcb_anc_m2c_call_log |
Called to update call log |
rcb_anc_m2c_change_theme |
Called to change the cluster theme |
rcb_anc_m2c_config_status |
Called to notify the cluster that WiFi/BLE name changed |
These functions are documented in detail in the below sections. It is important for the application to implement these functions correct for proper operation of the system.
Implementation Guide
This section provides an example about how to utilize the RAPIDSEA ANC stack to communicate between the mobile and cluster. Developers can integrate ANC functionality into their current applications by including the rs_anc.c in source code mode or the rs_anc.lib in the library mode.
The rs_anc.h header contains all API information, including cluster-to-mobile and mobile-to-cluster communication.
High level flow chart is depicted below for ANC stack:
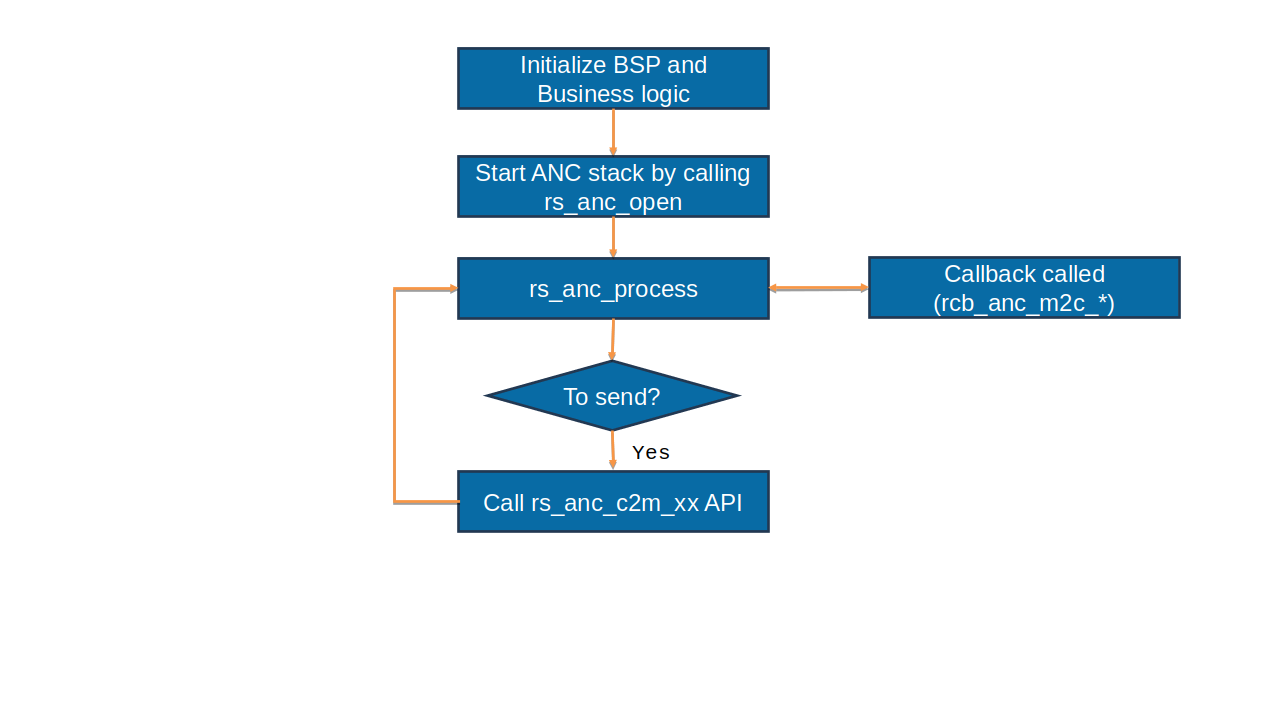
Assume we have to perform a simple demo where the Odometer data has to be communicated to the mobile app periodically and incoming message notification has to be received in the cluster.
The following code snippet explains the flow.
As it can be seen the code essentially,
Call rs_anc_open (&anc_instance, &anc_config) to initialize the ANC stack.
rs_anc_process (&anc_handle) should be called regularly.
Read the ODO meter information from vehicle and send it via rs_anc_c2m_send_vehicle_data.
If the message is received from the mobile, the rcb_anc_m2c_msg() callback is triggered.
Ensure that the Communication Module is programmed with the right firmware.
Now install the SAM application in your mobile app and connect to the Communication Module via the Bluetooth. It can be seen that the ODO information is updated in the Home screen of the mobile app.
Now send a message to the mobile app and notice the callback function rcb_anc_m2c_msg being called.
Running ANC over RTOS
It is possible to run the ANC stack with or without the OS. In case an RTOS is used, create a task with the required stack size initialize the stack t start of the task and continuously call the process function. For example, with FreeRTOS, a task for ANC stack with the given stack size and priority can be created and executed like the following example snippet:
/*anc_process task creation*/
if (xTaskCreate((TaskFunction_t)anc_demo_process, /* pointer to the task */
(char const *)"anc_demo_process", /* task name for kernel awareness debugging */
ANC_TASK_STACK_SIZE / sizeof(portSTACK_TYPE), /* task stack size */
NULL, /* optional task startup argument */
ANC_TASK_PRIORITY, /* initial priority */
&process_anc_handle /* optional task handle to create */
) == pdPASS)
{
printf("anc_demo_process creation success\r\n");
}
else
{
printf("anc_demo_process create failed!\r\n");
}
The function anc_demo_process() should include all core APIs and the following is an example snippet,
void anc_demo_process ()
{
anc_config.port = RS_SPI_UNIT_1;
anc_config.chip_sel_num = RS_SPI_CHIP_SELECT_NUM_0;
anc_config.chip_sel_ctrl = RS_SPI_CHIP_SELECT_ACTIVE_LOW;
anc_config.role = RS_SPI_ROLE_MASTER;
anc_config.non_blocking = RS_SPI_NON_BLOCKING;
anc_config.mode = RS_SPI_MODE_0;
anc_config.baud_rate = 5000000; // 5Mhz
anc_config.module_status_port = RS_GPIO_PORT_00_INDEX; /*!< Port to which the interrupt from Comm module is connected*/
anc_config.module_status_pin = 2; /*!< Pin to which the interrupt from Comm module is connected*/
anc_config.cluster_status_port = RS_GPIO_PORT_00_INDEX; /*!< Port to which the output from cluster is connected*/
anc_config.cluster_status_pin = 3; /*!< Pin to which the output from cluster is connected*/
//Open the connectivity stack
anc_handle = rs_anc_open(&anc_instance, &anc_config);
while(1)
{
rs_anc_process (anc_handle);
//Other business logic
//Call rs_anc_c2m_* API's as necessary
}
}
Running ANC over Baremetal
In case a bare metal system is used, the same can be split into two sections – one for initialization that is called only once and another for continuous processing.
void anc_demo_app_init()
{
anc_config.port = RS_SPI_UNIT_1;
anc_config.chip_sel_num = RS_SPI_CHIP_SELECT_NUM_0;
anc_config.chip_sel_ctrl = RS_SPI_CHIP_SELECT_ACTIVE_LOW;
anc_config.role = RS_SPI_ROLE_MASTER;
anc_config.non_blocking = RS_SPI_NON_BLOCKING;
anc_config.mode = RS_SPI_MODE_0;
anc_config.baud_rate = 5000000; // 5Mhz
anc_config.module_status_port = RS_GPIO_PORT_00_INDEX; /*!< Port to which the interrupt from Comm module is connected*/
anc_config.module_status_pin = 2; /*!< Pin to which the interrupt from Comm module is connected*/
anc_config.cluster_status_port = RS_GPIO_PORT_00_INDEX; /*!< Port to which the output from cluster is connected*/
anc_config.cluster_status_pin = 3; /*!< Pin to which the output from cluster is connected*/
//Open the connectivity stack
anc_handle = rs_anc_open(&anc_instance, &anc_config);
}
The below call can be called continuously.
int main
{
//HAL Init
//Other App logic init
anc_demo_app_init();
while(1)
{
//Other business logic
rs_anc_process (anc_handle);
//Call rs_anc_c2m_* API's as necessary
}
}
Dependency
This stack depends on the below RAPIDSEA modules/interfaces/utils that can be obtained or custom implemented.
ANC Header Details
Documentation from the relevant header as follows:
Warning
doxygenfile: Cannot find file “rs_anc.h